Embedded lending has the potential to address the issue of growing financial exclusivity. Financial inclusivity is required to grow the top-line requirements of SMEs involved in areas like retail trade, farming, logistics and mining. Having an access to capital helps support fixed costs and benefits businesses in maximizing profits. This profitability invariably results in retained earnings that are re-invested into the economy to encourage further growth.
Many businesses have faith in the potential of embedded lending to reinforce their revenue by 5x in the future.
Decoding Embedded Lending
Embedded Lending refers to the financial services incorporated into non-financial products, removing the need for intermediaries which allow users to quickly and seamlessly borrow money (such as retail or food delivery apps). Removing intermediaries allows the entire loan ecosystem to become lighter offering a seamless user experience.
Embedded lending transforms the way that credit is distributed, moving it from a horizontal model in which acquiring new customers directly cost more and more money to a vertical model in which SaaS and eCommerce deliver credit at essentially zero marginal cost.
Embedding also provides "digital platforms" data, which enables loans to be issued proactively when customers are likely to need them. This data richness is unmatched for underwriting and pricing.
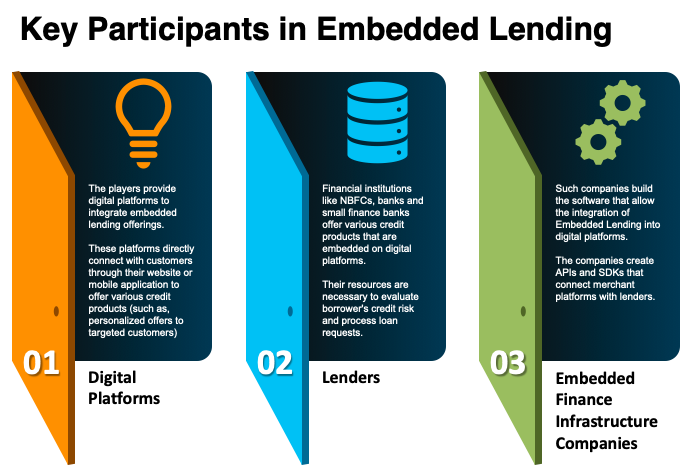
How Big is the Opportunity?
Embedded lending, a new value chain, has put traditional institutions at risk of changing economics and unfavourable choices as it is still in it’s infancy stage. Despite the risk involved, businesses can take advantage of great development potential, particularly if they decide where to play in various vertical segments.
The global embedded lending market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 27.5% from $51.9 billion in 2022 to $199.9 billion in 2029. This opportunity to serve the new lending value chain will eventually result from investing in the appropriate competencies.
However, the drawbacks of incorporating embedded lending into the non-financial platforms include insufficient infrastructure as well as unavailability of regulatory licenses to perform the lending operations. The structure is either atrociously designed or produces unfavourable incentives due to a lack of knowledge and poor execution.
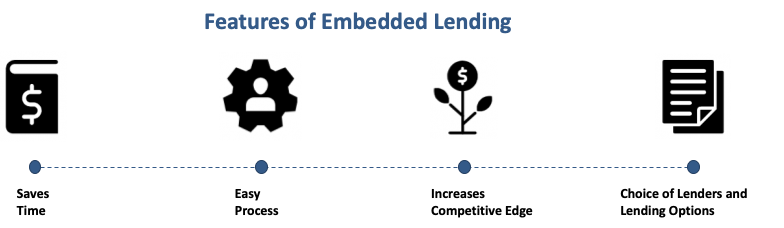
Let’s look into the features of embedded lending to help understand why our economy needs embedded lending that will help grow and support its end customers with the latest fintech features.
How does Embedded Lending help businesses?
Embedded lending enables companies to provide a seamless customer experience that adds value by increasing customer engagement, retention, and lifetime value (LTV) in the process. Companies that use integrated lending are in the ideal position to meet their clients' capital needs since they have the best customer knowledge of everyone.
The modern-age companies can boost their clients' chances of getting a loan approved by utilising the information they currently have on them, such as payroll, payment, and spending data. Given this, successfully integrated lending needs a lending partner that can not only provide the lending infrastructure but also support businesses in the analysis of crucial consumer financial data.
The goal of embedded lending is to simplify the process for end-user to access financial services as and when required. Embedded lending can be used in a variety of fields, including:
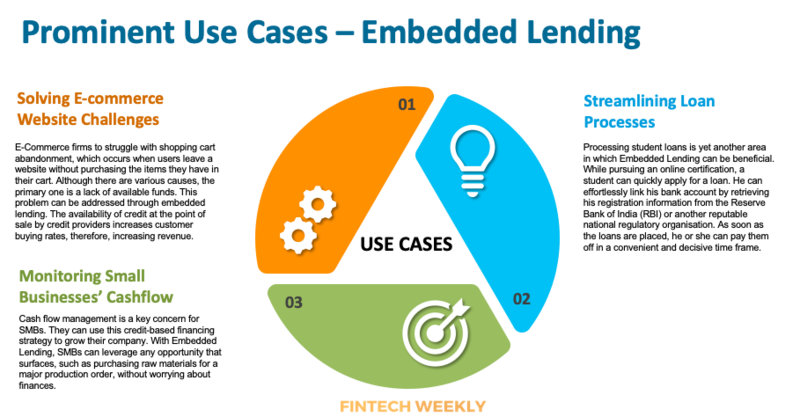
The Way Forward
The lending sector is focusing on embedded banking and services to engage customers at the grassroots levels using innovation and technology. Both non-financial institutions and financial institutions will gain from the vertical integration of banks and fintech, which will bring a powerful revolutionary shift in the sector across borrowing, investing, and payments.
The emphasis of tomorrow's lending leaders is specifically on redesigning the digital lending experience strategy and expanding digital services while also retaining and strengthening client loyalty. Financial institutions, banks, and lenders are examining a wide range of issues while automating lender-borrower interactions across channels.
Embedded lending is proven as a remarkable fintech breakthrough that every company should capitalise on to improvise their revenue streams. The synergy it creates will benefit both financial and non-financial institutions.












